Data Model
Application Database
The application database epigraf holds data that is independent of any specific project.
The tables include:
- databanks: The configured project databases.
- users: User data, including contact information and settings
- permissions: User permissions, see Authentication and authorization.
- files: Metadata for files managed by Epigraf.
- docs: Wiki, help and public pages.
- pipelines: Export pipeline configurations.
- jobs: Each batch operation generates a job.
See the entity classes in src/model/Entity for further information about the available fields in each table.
Project Databases
Each project has its own database, prefixed with epi_.
Project databases implement the Relational Article Model (RAM)
which includes the following tables:
- projects: A project groups articles together, for example the articles of a volume.
- articles: An article contains data organized in metadata and sections.
- sections: A section is part of an article and contains data organized in items. Sections can be nested.
- items: An item is a unit of information within a section. It contains fields for data (text, values), references to properties, or references to articles or sections.
- footnotes: Text fields (items) can contain footnotes (notes and critical apparatus). Footnotes are placed as tags in text fields and assigned an ID. The content can be found under this ID in combination with the name of the table and the field in the footnotes table.
- links: Text fields (items) can contain annotations, i.e. tags with a link to articles, sections, properties, and footnotes and other attributes. The links table contains a record for each tag, linked by the tag ID, field name, table name and table ID.
- properties: Properties contain supporting data and vocabularies. Properties are organized in hierarchies. For example, a property can be a place name or a category for content analysis.
- types: The configuration of the domain model, including article types and available fields.
- files: Files are stored in the file system and mirrored in the database.
- notes: Notes contain pages used for collaboration and documentation in a team.
See below and see the entity classes in plugins/Epi/src/model/Entity for further information
about the available fields in each table.
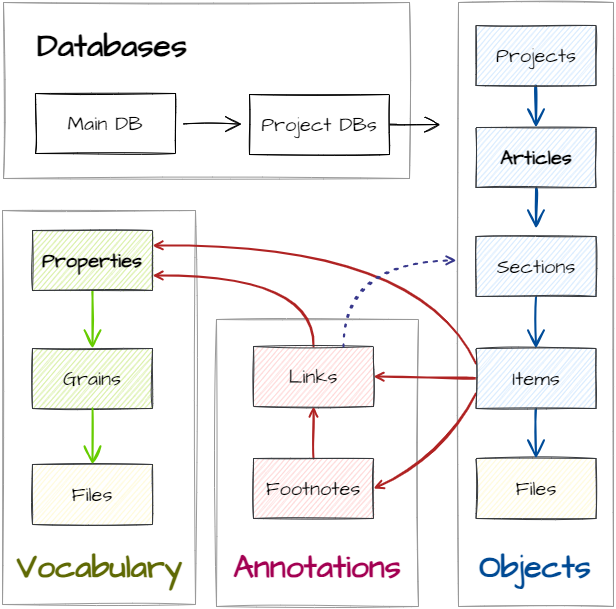
Structure of the Project Databases
The Relational Article Model (RAM) distinguishes between data model and domain model. The data model provides abstract elements for modelling texts and objects. The domain model maps these elements to a specific use case by a type configuration.
After creating a new project database, it should be configured for the specific domain.
This configuration is stored in the types-table for each project database and,
for example, defines field labels. The configuration is stored in JSON format in the config field.
See the user help for further information about configuring the domain model.
In the database, each project, article, section, item, property, note, and user record has a type-field which
connects it to the configuration. In the types-table, in turn, the scope corresponds to the table name
and the name to the specific type. The overview below lists these type-fields:
| Table | Column | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| projects | projecttype | Type of the project. | epi |
| articles | articletype | Type of the article. | object|text |
| sections | sectiontype | Type of the section. | text |
| items | itemtype | Type of the item. Items can contain text (e.g., transcriptions), files (e.g., images), or categorizations using properties (e.g., locations, font types, object types). | transcriptions |
| properties | propertytype | Type of property. Properties include vocabularies and categories for describing objects. A property type specifies a category system (e.g., locations, fonts, object types). | materials |
| notes | notetype | Type of note. | |
| users | usertype | Type of user. | author|reader|devel |
Types
The types table configures the domain model, i.e., the types of articles, sections, items, footnotes, links, and
properties that exist in the domain.
Each type defines which of the fields in the other tables are used, how they are labeled
and what type of data they contain. For example, the content field in the items table
can contain plain text, XML or JSON, as defined in the config field.
| Column | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| scope | Name of table to which the configuration refers | projects|articles|sections|items|properties|notes|users|grains |
| name | Name of the article, section, item, link, or property type | fonttypes |
| caption | Label of the type | Schriftarten |
| config | Configuration of the type: Defines which fields are used and how they are labeled (domain model) | {"items":["images"],"view":"images","links":{"comment":["text","transcription","references","links"]}} |
| mode | For different display modes (default, preview, revise), different configurations for the same type as denoted by scope and name may be used. | default |
| preset | Presets support different configurations for the same type as denoted by scope and name. | default |
| sortno | Indicates the order of types. | 1 |
| category | Category for structuring the types. | vocabulary |
| description | Further explanations on how the type is used. | Wird in Inschriftenartikeln bei Textabschnitten für den Namen des Abschnitts verwendet. |
General Fields
The following fields are present in each table:
| Column | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| id | Unique internal database number of the row | 123 |
| deleted | 0 = Record is not deleted, 1 = Soft-deleted, 2 = Old version (soft-deleted using version_id), 3 = Manually deleted in a data cleanup |
0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| version_id | ID of the original row | 123 |
| job_id | If the entry was created or modified by the job system: ID of the job in the Epigraf database | 123 |
| published | 0 = Drafted (not publicly accessible) 1 = In progress, entry ist being actively worked on (not publicly accessible) 2 = Complete, finished data collection and editing (not publicly accessible) 3 = Published (publicly accessible but not searchable) 4 = Searchable (publicly accessible and searchable) |
0 | 1 | 4 |
| created | Timestamp of row creation | 10.10.2012 10:10 |
| modified | Timestamp of the last modification | 10.10.2012 10:10 |
| modified_by | ID of the user who last modified the row | 123 |
| created_by | ID of the user who created the row | 123 |
| norm_data | IRIs of standardized identifiers, e.g., DOIs. Multiple IRIs are separated by line breaks. | |
| norm_iri | IRI-Fragment of the row. In combination with the table name and the row type, the IRI uniquely identifies a row in the Epigraf universe. |
The following fields, if present, order and organise rows:
| Column | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| sortno | Number for sorting rows | 1 |
| parent_id | ID of the parent row or NULL for root nodes | 123 |
| level | Level in the hierarchy, starting with 0. | 0|1|2 |
| lft | Left value of the modified preorder tree traversal structure (MPTT), starting with 1. | 4 |
| rght | Right value of the modified preorder tree traversal structe (MPTT). | 6 |
Projects
Projects group articles.
| Column | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| name | Name of the project | Greifswald |
| signature | Abbreviation of the project name | hgw |
| description | Details about the project (JSON) |
Articles
Each article is a description of one analysis unit. Articles contain sections.
| Column | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| signature | Short name or number of the article | hgw.bodendenkmalpflege.glasbecher|008 |
| name | Title of the article | Glasbecher |
| status | Indicates editing progress | newly created |
| projects_id | ID of the associated project (foreign key). | 1 |
Sections
Sections are parts of an article. Sections are sorted and arranged hierarchically. They contain items.
| Column | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| name | Section title, automatically generated based on the caption-field in the types-table depending on the section type, or manually created. | Inschrift A |
| number | Number of the section within an article. | 1 |
| sortno | The position of the section within its article. | 12 |
| comment | Meta-field for notes about the section | Transcription needs work |
| alias | Deprecated. Manual override of automatically generated names in the name-field | Erste Inschrift |
| status | Depracated: Use the published field. Meta-field for recording the processing status (0=unprocessed; 1=started; 2=completed; 3=verified) | 0|1|2|3 |
| layout_cols | Width of the grid for arranging items (e.g., coats of arms), see pos_y field in the items-table. | 2 |
| layout_rows | Height of the grid for arranging items (e.g., coats of arms), see pos_y field in the items-table. | 3 |
| articles_id | Unique ID of the associated article (foreign key). | 123 |
Items
Items capture the contents of sections and articles. Each item represents one snippet of information. Depending on the type of information, different fields are used and configured in the types table. They include fields for text (plain, JSON, XML), files, references to properties, and links to articles or sections.
Fields may contain XML such as footnotes markup or JSON for nested values, if configured in the types table.
| Column | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| sortno | Order of items when multiple items of the same type are included in a section. | 2 |
| itemgroup | Groups items within a section. Items belonging to the same group have the same value. | |
| value | Only used when the item contains small text or numeric values. May contain XML or JSON. | 0,3 |
| content | Only used when the item contains text. May contain XML or JSON. | an<abr id="000004126348876084490740744071" value="">n</abr>o |
| translation | Only used when the item contains text. Holds the translation of the text. May contain XML or JSON. | Im Jahr |
| flagged | Binary marker. Used, for example, to indicate whether images should be included in image section (Abbildungsteil). | 0|1 |
| properties_id | Only used when the item refers to a property. Unique ID of the row in the properties table (foreign key). | 123 |
| links_tab | Only used when the item refers to another section, article, or item. Contains the table name of the linked row. | sections |
| links_id | Only used when the item refers to another section, article, or item. Contains the ID of the linked row from the table specified in links_tab (polymorph foreign key). | 123 |
| links_field | Not used. | |
| links_tagid | Not used. | |
| file_name | Only used when the item contains a file. Specifies the name of the file. | hst.nikolai.gp-storkow_004.jpg |
| file_type | Only used when the item contains a file. Specifies the file type. | .jpg |
| file_path | Only used when the item contains a file. Contains the file path. The root directory is defined in the types-table. Path must not begin or end with slashes. | hst/006 |
| file_source | Only used when the item contains a file. Path to the local file (before it was uploaded to Epigraf). | Z:\Epigraf-inschriften_mv\Bilder\hwi\hwi.alteschule.predella\ |
| file_meta | Only used when the item contains a file. Holds additional metadata, such as creator, artist, license, etc. Usually in JSON-format. | |
| file_copyright | Deprecated, use file_meta. Only used when the item contains a file. Contains copyrights information for the file, e.g. a photographer’s name. Can contain XML. | LAKD/AD |
| file_online | Only used when the item contains a file. Indicates whether the file is stored on the Epigraf server (-1) or locally (0). | 0|-1 |
| date_sort | Only used when the item includes a date. Contains a sorting key for chronological sorting of items. Derived from date_value. | 1400ABD0000000A3 |
| date_value | Only used when the item includes a date. Contains the date or time period of the date, as text. | 2.H.14.Jh. |
| date_start | Only used when the item includes a date. Contains the start year of the date. | 1350 |
| date_end | Only used when the item includes a date. Contains the end year of the date. | 1400 |
| date_add | Only used when the item includes a date. Contains additional information about the date. May contain XML. | Datierung nach der Fundschicht |
| source_autopsy | Indicates whether the item content originates from the editor (1) or from someone else (0). | 0|1 |
| source_from | Indicates from where the item content originates (source_autopsy = 0). For example, a reference to literature. Can contain XML. | Foto LAKD |
| source_addition | Additional information about the data origin, e.g. a page number in a book (see source_from). Can contain XML. | Hs. 245 |
| pos_x | Horizontal position of the item in a grid (e.g., a coat of arms), see sections-table layout_cols-field. Counting begins with 1. | 2 |
| pos_y | Vertical position of the item in a grid (e.g., a coat of arms), see sections-table layout_rows-field. Counting begins with 1. | 3 |
| pos_z | Order of items in a grid when multiple items occupy the same position. Counting begins with 1. | 1 |
| articles_id | ID of the row in the sections-table (foreign key). | 123 |
| sections_id | ID of the row in the articles-table (foreign key). | 123 |
Footnotes
Footnotes are added as tags in text fields, assigned with an XML ID. The footnotes table contains the content and the XML ID in the tagid field.
| Column | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| name | Number or letter of the footnote | c |
| segment | Reference text | et |
| content | Content of the footnote | Hier und im Folgenden bei Chytraeus tironisches et. |
| root_tab | If the footnote is in an article: “articles”. If the footnote is in the properties: “properties”. | articles|properties |
| root_id | If the footnote is in an article: ID of the article row. If the footnote is in a properties row: ID of properties row. | 123 |
| from_tab | Origin of the footnote, table name. | items |
| from_id | Origin of the footnote, ID of the row . | 289225 |
| from_field | Origin of the footnote, field name in the table. | content |
| from_tagname | Origin of the footnote, name of the tag within the XML-field, as configured in the types. | app1|app2 |
| from_tagid | Origin of footnote, ID of the XML-Tag. | 000004453145122674768518563255 |
| from_sort | Number of the tag within the XML-field | 3 |
Links
The links table contains annotations that refer to properties, articles, sections or other tables. Tags are assigned an ID to be found as tagid in the links table.
| Column | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| to_tab | Target of the reference, name of the target table | sections |
| to_id | Target of the reference, ID of the target row | 270045 |
| to_field | Target of the reference, name of the field in the target table row | |
| to_tagid | Target of the reference, ID of an XML tag within the target field | |
| root_tab | If the link is in an article: “articles”. If the link is in a property: “properties”. | articles |
| root_id | If the link is in an article: ID of the article. If the link is in a property: ID of the property. | 5 |
| from_tab | Origin of the reference, name of the table | items |
| from_id | Origin of the reference, ID of the row | 289225 |
| from_field | Origin of the reference, name of the field in the table | content |
| from_tagname | Origin of the reference, name of the tag within the XML-field, as configured in the types. | z |
| from_tagid | Origin of the reference, ID of the XML tag. | 000003957386834346064814828763 |
Properties
The properties table contains categories and vocabularies. A property is a specific category (e.g., Marienkirche Greifswald, gotische Minuskel, Kelch) within a category system (see propertytype) or a relationship between properties.
Properties are sorted and hierarchically organized. A category can have super-categories (parent lemma / Oberlemma) or sub-categories (child lemma / Unterlemma).
The property order is fixed by the tree structure. If a different order is needed when exporting data, the sort key can be used. The sort key is a text field. To sort numbers ascending, single-digit numbers should be prefixed with leading zeros.
Properties are either referred to in items (properties_id) or linked from XML-fields (to-fields).
| Column | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| lemma | The property caption. | geschnitzt |
| name | Long name of the property. The name contains, compared to lemma, the complete path. | Holz, geschnitzt |
| sortkey | Key for sorting, usually identical to lemma. | Bispinghof 09 |
| signature | A short name or number of the property. | |
| unit | Unit of the property, used for measurements, e.g. to define the unit weights as kg. | kg |
| comment | Details about the property. May contain XML. | HST: Estherteppich |
| content | Details about the property. May contain XML. | Frau mit Blumenstrauß |
| elements | Deprecated, use XML or JSON in the content field. Details about the property as configured in the types. | drei Blumen |
| file_name | Only used when the property refers to a file. Contains the file name. | hst/hm.hst.nikolai.chorschranken.s21.m1.svg |
| keywords | Keywords to search the property. | hgw |
| source_from | Origin of the property information. | vgl. <rec_lit id="12345" value="Siebmacher's Wappenbuch"></rec_lit> (ND) 9 |
| iscategory | Indicates whether the property contains content (0) or is a structural category (1) | 0\|1 |
| ishidden | Indicates whether the category should be displayed in published data (0) or not (1) | 0\|1 |
| related_id | For references between properties (“see also”), the ID of the related property. | 123 |
| properties_id | Metaproperty for categorizing properties. ID of the property in the properties-table. | 123 |
| mergedto_id | Used when records are merged. ID of the merged, new entry. | 123 |
| splitfrom_id | Used when records are split. ID of the original entry. | 123 |
Files
The files table mirrors the file system on the server to maintain file and folder names in the database.
| Column | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| name | File or folder name | dsc08032.jpg |
| description | Description of file or folder | This folder is for... |
| type | File extension. Empty if folder. | jpg |
| size | File size in bytes. Empty if folder. | 3506176 |
| root | Mount point: Segregated areas where files are located and to which path and name refer | articles|properties|notes|root |
| path | Indicates file path. Must not contain slashes at beginning or end. | |
| isfolder | Indicates whether it’s a folder (1) or file (0) | 1|0 |
Notes
The notes table contains pages for collaboration in a team.
| Column | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| name | Title of the note | Adressen Wismar |
| category | Category (menu item) | Organisation |
| sortkey | Key for sorting | |
| content | Content of the note | Planungsbüro X |
Users
The users table contains information about the editors. The norm_iri of the user row should be present in the application database’s user table.
| Column | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| name | Editor’s name | Jakob Jünger |
| acronym | Initials of the name | JJ |
Meta
The metadata table contains additional information about the database in the form of key-value pairs.
| Column | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| name | Key of the entry | db_version|db_name |
| value | Value of the entry | 4.4|Epigraf |
Further tables and columns are either deprecated or experimental.