View
Depending on the rendering format, as determined by the URL extension or the request Accept header, different view classes are used.
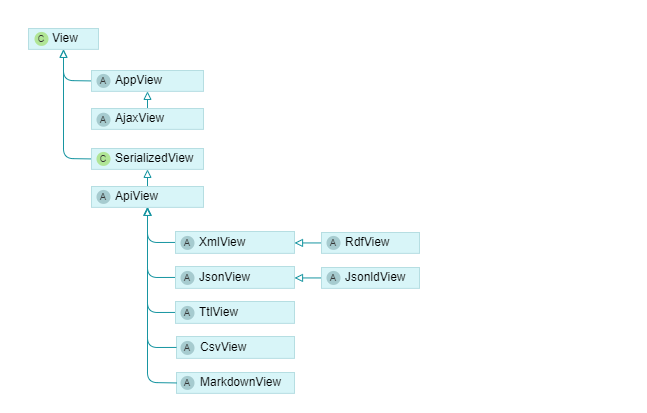
- AppView: Renders HTML pages for the browser and directly inherits from CakePHP’s View class. AjaxView is a subclass of AppView that omits layout rendering.
- ApiView: The base class for rendering structured data formats like JSON or XML, derived itself from CakePHP’s SerializedView class. The ApiView based classes are also used in the export pipelines to generate TEI-documents and other structured data formats.
Rendering HTML for the Browser
The AppView class uses templates to render HTML pages, located in the templates directory
and named after the controller and action, see for example templates/Users/index.php.
This is a CakePHP convention. Some actions change the convention by calling $this->render()
with a template name directly in the controller. This way, templates can be shared between actions,
for example to always use the same template for public pages, help pages, and wiki pages.
The AppView class embeds the page content into a layout which is located in the templates/layout directory.
Templates for the project databases are located in the plugins/Epi/templates directory.
Shared rendering logic is encapsulated in helper classes, which are located in the src/View/Helper directory
on the application level and in the plugin folders.
Support for rendering of entity collections in tables:
- TableHelper: Generates tables for entities, entity collections and arrays.
- TreeHelper: Generates tree markup, e.g. for categories. The helper supports trees for selecting entities. Can be used in combination with the table helper to add tree markup to tables.
Support for rendering of entities and their fields:
- BaseEntityHelper: The class is central to rendering entities.
Its function
entityForm()is called to view entities and to create input forms. Its functionsectionList()is called for generating documents such as articles. - EntityHtmlHelper: Derives from BaseEntityHelper helper for markup specific to non-editing HTML output for entities.
- EntityInputHelper: Derives from BaseEntityHelper helper for form input generation when editing entities.
- EntityMarkdownHelper: Derives from BaseEntityHelper helper and overrides functions for Markdown rendering.
Utilities for rendering HTML elements:
- ElementHelper: Provides basic functions for creating HTML tags.
- LinkHelper: Generates links and buttons.
- MenuHelper: Generates different kinds of menus with the function
renderMenu(). - FilesHelper: Supports uploading files, displaying previews and thumbnails.
- TypesHelper: Provides access to the types configuration.
Rendering API Data
JSON, XML, CSV
The base formats for API access are JSON, XML and CSV. Epigrafs supports rendering the full database content with all fields in those formats. Therefore, the formats can be used to import and export data.
For collections, only columns selected in the query parameters are rendered. Columns are configured using extraction keys in the types configuration.
For entities, the rendered fields are determined by the entity’s type.
RDF, JSON-LD, Turtle
From the base formats, triple formats are derived in the RdfView, JsonLdView, and TtlView classes. For collections, the hydra standard is used. For entities, the generated triples have to be configured in the types on the project database level.
Markdown
The MarkdownView class is used for generating plain text from the database content. This may prove useful for full text search indexes and machine learning approaches, for example, to use and train large language models.